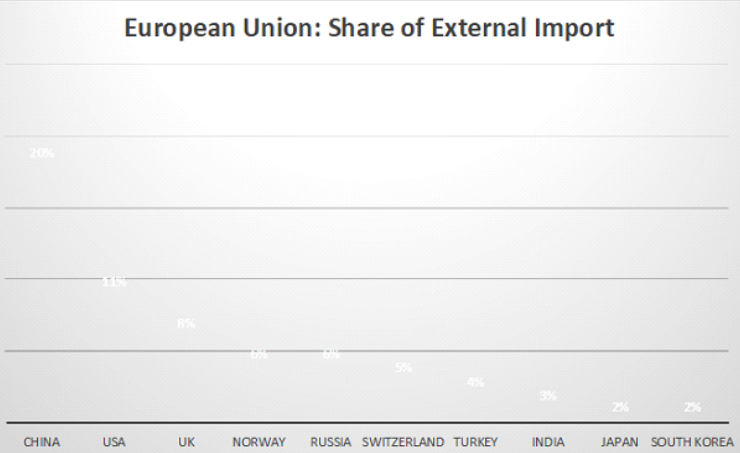
China is the largest external exporting country to the EU with a share of 20%. China’s remarkable success in exports to the EU can be attributed primarily to its cost advantage. The nation boasts comparatively lower labor costs in contrast to numerous developed countries and many emerging or developing nations. This cost efficiency empowers Chinese manufacturers to create goods at more affordable prices, appealing to global buyers in search of budget-friendly products. The substantial development underway in China is fueled by its massive population, exceeding one billion people, with 820 million poised to contribute to the labor force.
EU companies often opt to outsource their production and supply chain activities to countries such as China, Turkey and India primarily driven by cost-saving measures and access to cheaper labor. The lower operational expenses in these regions contribute significantly to the economic efficiency of European businesses. However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that this outsourcing trend may raise concerns about Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) issues through outsourced supply chain activities. Less developed countries may struggle with challenges related to labor conditions, human rights, and environmental standards. The pursuit of cost advantages should be balanced with a commitment to responsible and sustainable business practices to address potential ESG violations that may arise from outsourcing to regions with such issues.
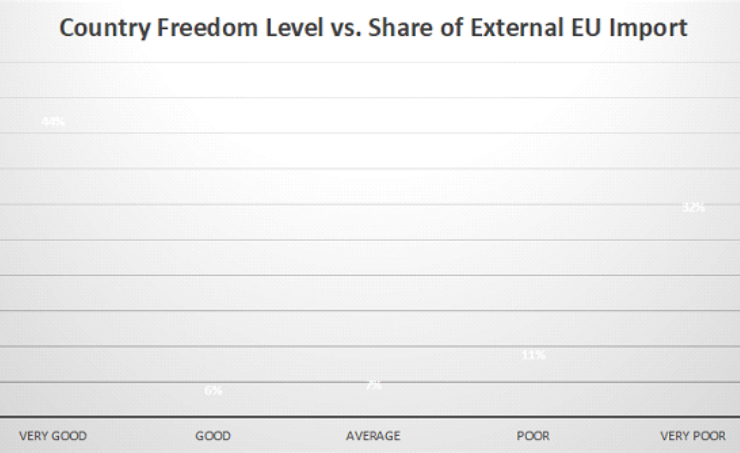
The revelation that 43% of the European Union’s external imports originate from countries marked by poor or very poor levels of freedom, particularly concerning political and civil rights, underscores the ethical challenges entwined with global trade relationships. To navigate these challenges, companies must prioritize due diligence assessments before outsourcing supply chains to nations with compromised freedom levels. Rigorous evaluations should encompass a holistic examination of political and civil rights indicators, prompting companies to consider government transparency, respect for human rights, and adherence to the rule of law. Moreover, businesses should establish and uphold comprehensive code of conduct policies, setting explicit standards for ethical behavior throughout the supply chain. This not only serves as a proactive measure to prevent potential issues but also positions companies as champions of responsible business practices.
Failing to address human rights abuses or civil rights violations within the supply chain can result in severe consequences. Reputational damage is a significant risk, as consumers increasingly scrutinize the origins of products and may boycott brands associated with unethical practices. Legal repercussions, including fines and regulatory interventions, become likely as authorities scrutinize supply chain ethics. Real-world examples abound, such as instances of child labor, unsafe working conditions, or environmental negligence, leading to public backlash and financial repercussions for specific suppliers. Embracing ethical standards in supply chain management is not just a matter of risk mitigation but a strategic imperative for businesses looking to uphold values, build trust, and contribute to a sustainable and responsible global trade ecosystem.
ESG Reporting Intelligence is the solution for companies to manage supply chain issues. By enlisting the supply chain on the platform, the risk related to the individual supplier can be analysed on the basis of the response from the supplier about how they comply with the company’s policies in chosen criteria assessments. Further, ESG Reporting Intelligence can provide feedback to the work related to supplier management with the purpose of optimising the benefits for the company.
Contact details
Niels Jensen – ESG Consultant
Niels.J@esgri.com
+45 4252 3762
Copenhagen, Denmark
Bibliography
OEC World
Available at: https://oec.world/en/profile/international_organization/european-union?depthSelector5=HS4Depth&yearSelector5=2022&extraTradeFlowSelector=flow1
[Accessed 12 March 2024].
Freedomhouse
Available at: https://freedomhouse.org/explore-the-map?type=fiw&year=2024
[Accessed 12 March 2024].
Uniaircargo
Available at: https://www.uniaircargo.co.id/blog/7-reasons-why-china-became-the-biggest-exporter-in-the-world-432
[Accessed 12 March 2024].